Rho Bootis
| Rho Bootis (ρ) | |
 | |
| Observationsdata Epok: J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Stjärnbild | Björnvaktaren |
| Rektascension | 14t 31m 49,787962s[1] |
| Deklination | +30° 22′ 17,1781″[1] |
| Skenbar magnitud () | 3,59[2] |
| Stjärntyp | |
| Spektraltyp | K4 III[3] |
| U–B | +1,44[2] |
| B–V | +1,30[2] |
| R–I | 0,65 |
| Astrometri | |
| Radialhastighet () | -13,57 ± 0,19[4] km/s |
| Egenrörelse (µ) | RA: -100,90[1] mas/år Dek.: +120,73[1] mas/år |
| Parallax () | 20,37 ± 0,18[1] |
| Avstånd | 160 ± 1 lå (49,1 ± 0,4 pc) |
| Absolut magnitud () | +0,27[3] |
| Detaljer | |
| Massa | 1,0 - 1,4[5] M☉ |
| Radie | 21,57 ± 0,25[5] R☉ |
| Luminositet | 131,9 ± 6,8[5] L☉ |
| Temperatur | 4 398 ± 56[5] K |
| Metallicitet | -0,19 ± 0,10[6] dex |
| Ålder | 10,11 ± 2,82[6] miljarder år |
| Andra beteckningar | |
| ρ Boo, 25 Bootis, BD+31° 2628, FK5 534, HD 127665, HIP 71053, HR 5429, SAO 64202 | |
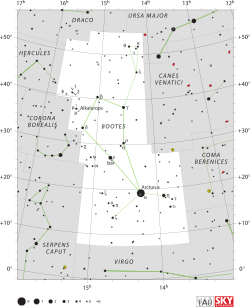
Rho Bootis (ρ Bootis, förkortad Rho Boo, ρ Boo), som är stjärnans Bayer-beteckning, är en ensam stjärna[7] i mellersta delen av stjärnbilden Björnvaktaren. Den har en skenbar magnitud av 3,59[2] och är synlig för blotta ögat där ljusföroreningar ej förekommer. Baserat på parallaxmätning inom Hipparcosuppdraget på ca 20,4 mas,[1] beräknas den befinna sig på ett avstånd av ca 160 ljusår (49 parsek) från solen. Sedan 1943 har spektret för stjärnan fungerat som en av de stabila referenspunkter som andra stjärnor klassificeras efter.[8]
Egenskaper[redigera | redigera wikitext]
Rho Bootis är en orange till gul jättestjärna av spektralklass K4 III,[3] som för närvarande befinner sig på den röda jättegrenen. Den har en massa som är ca 1,2[5] gånger större än solens massa, en radie som är ca 22[5] gånger solens radie och avger ca 132[6] gånger mer energi än solen från dess fotosfär vid en effektiv temperatur på ca 4 300 K.[7]
Rho Bootis har en optisk följeslagare, en stjärna av magnitud 11,5, som ligger separerad med 34,7 bågsekunder vid en positionsvinkel på 345° (år 2013).[9]
Referenser[redigera | redigera wikitext]
- Den här artikeln är helt eller delvis baserad på material från engelskspråkiga Wikipedia, 15 april 2019.
Noter[redigera | redigera wikitext]
- ^ [a b c d e f] van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357.
- ^ [a b c d] Jennens, P. A.; Helfer, H. L. (September 1975), "A new photometric metal abundance and luminosity calibration for field G and K giants", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 172: 667–679, Bibcode:1975MNRAS.172..667J, doi:10.1093/mnras/172.3.667.
- ^ [a b c] Cardini, D. (January 2005), "Mg II chromospheric radiative loss rates in cool active and quiet stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 430: 303–311, arXiv:astro-ph/0409683, Bibcode:2005A&A...430..303C, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041440.
- ^ Massarotti, Alessandro; et al. (January 2008), "Rotational and Radial Velocities for a Sample of 761 HIPPARCOS Giants and the Role of Binarity", The Astronomical Journal, 135 (1): 209–231, Bibcode:2008AJ....135..209M, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/135/1/209.
- ^ [a b c d e f] Berio, P.; et al. (November 2011), "Chromosphere of K giant stars. Geometrical extent and spatial structure detection", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 535: A59, arXiv:1109.5476, Bibcode:2011A&A...535A..59B, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117479.
- ^ [a b c] Reffert, Sabine; et al. (2015), "Precise radial velocities of giant stars. VII. Occurrence rate of giant extrasolar planets as a function of mass and metallicity", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 574: A116, arXiv:1412.4634, Bibcode:2015A&A...574A.116R, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201322360, hdl:10722/215277.
- ^ [a b] Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008), "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 389 (2): 869–879, arXiv:0806.2878, Bibcode:2008MNRAS.389..869E, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x.
- ^ Garrison, R. F. (December 1993), "Anchor Points for the MK System of Spectral Classification", Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society, 25: 1319, Bibcode:1993AAS...183.1710G, hämtad 2012-02-04
- ^ Mason, Brian D.; et al. (2001), "The 2001 US Naval Observatory Double Star CD-ROM. I. The Washington Double Star Catalog", The Astronomical Journal, 122 (6): 3466–3471, Bibcode:2001AJ....122.3466M, doi:10.1086/323920.





